本文移植於tutortecho 2021年6月20日 撰寫
(本文章以本人學習筆記為主, 中英夾雜沒有期待有人看懂)
靜態多重派發的技術主要是仰賴 compiler 來達到,
multiple issue 的技術在硬體層面就是使用 duplicated hardware 來達到多人同時做多事的效能提升,
以下以 MIPS架構和 5-stage pipeline 設計來說明,
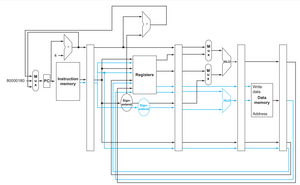
從圖中可以看到 execution stage 有兩個 ALU
並且 instruction decode stage 的 register file 多了一組 access port
在 ID 可以同時讀取(寫入)兩組指令的 gpr
在 EX 可以同時處理兩組指令
Instruction must be designed to ‘issue package’, that is VLIW (very long instruction word).
但此設計並不是那麼完美的可以任意同時處理兩種指令
同時執行 add 和 sub 會造成上方的 ALU 產生 structure hazard,
同時執行 load 和 store會造成下方 ALU 有structure hard,
所以 Compiler 設計 issue package 時要將 “arithmetic and branch" 與 “memory access" 指令分開.
Let me see a simple case, how would this loop be scheduled on current architecture by compiler ?
Before scheduled :

After scheduled :
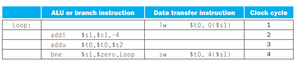
Cycle per instruction from 0.5 turn into 0.8, that sucks, so many data hazard (data dependency) there.
一堆 nops 插在 issue packet 裡面,
為了讓 dual-issue 效能更好,
compiler 有了迴圈展開 (loop-unrolling) 和 register-renamin 技術,
原本要做 20 圈的迴圈轉換成 5 圈 (每一圈做4倍的量)
想當然爾, 迴圈中要做4倍量所需要的 register (in high-level programming, it can be treated as variable)
程式碼就會轉換成如下,
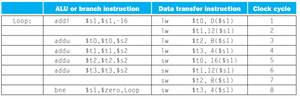
用 4個 registers 來儲存每一圈 load 出來的值,
在cycle 3, load to $t2 時可以同時使用 $t0 (load and write back done before)
利用 renaming 使用更多的 register 來避免發生 data dependency,
藉此可以讓每個 cycle 可以同時處理兩種指令
發表留言